Download Procyon (α Canis Minoris) Worksheets
Click the button below to get instant access to these premium worksheets for use in the classroom or at a home.
This worksheet can be edited by Premium members using the free Google Slides online software. Click the Edit button above to get started.
Download free sample
Not ready to purchase a subscription yet? Click here to download a FREE sample of this worksheet pack.
Resource Examples
Click any of the example images below to view a larger version.
Key Facts & Information
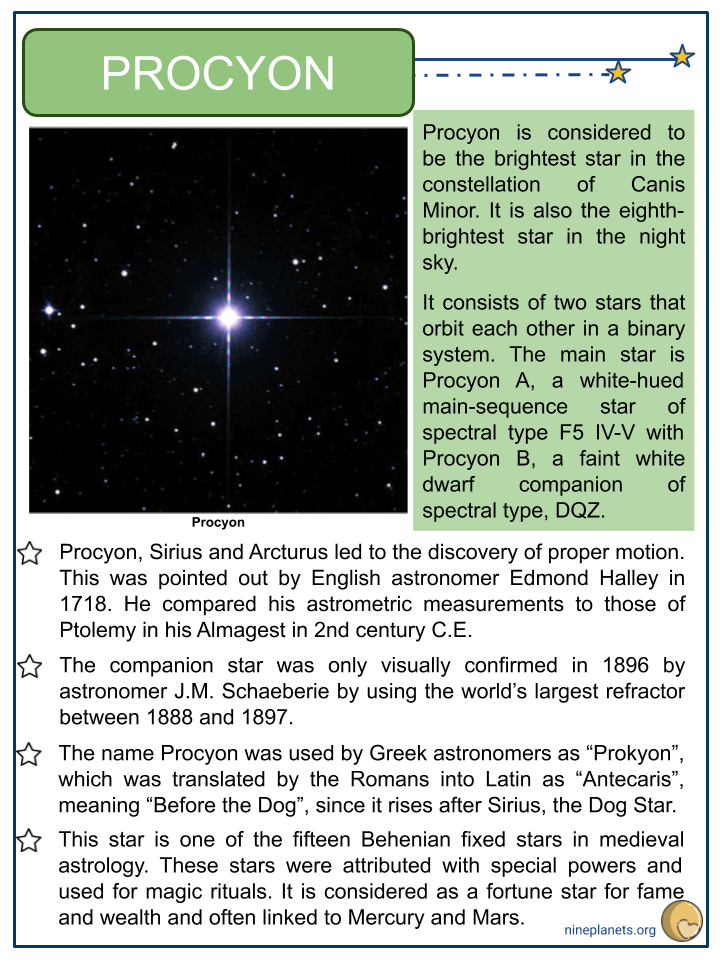
- Procyon is considered to be the brightest star in the constellation of Canis Minor. It is also the eighth- brightest star in the night sky.
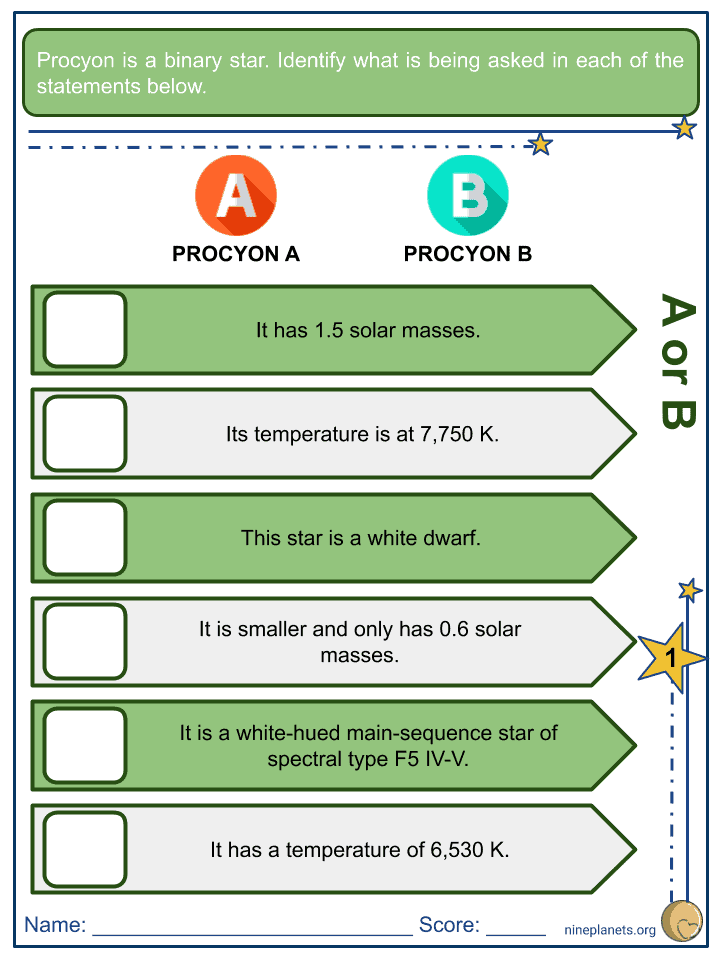
- It consists of two stars that orbit each other in a binary system. The main star is Procyon A, a white-hued main-sequence star of spectral type F5 IV-V with Procyon B, a faint white dwarf companion of spectral type, DQZ.
- Procyon, Sirius and Arcturus led to the discovery of proper motion. This was pointed out by English astronomer Edmond Halley in 1718. He compared his astrometric measurements to those of Ptolemy in his Almagest in 2nd century C.E.
- The companion star was only visually confirmed in 1896 by astronomer J.M. Schaeberie by using the world’s largest refractor between 1888 and 1897.
- The name Procyon was used by Greek astronomers as “Prokyon”, which was translated by the Romans into Latin as “Antecaris”, meaning “Before the Dog”, since it rises after Sirius, the Dog Star.
- This star is one of the fifteen Behenian fixed stars in medieval astrology. These stars were attributed with special powers and used for magic rituals. It is considered as a fortune star for fame and wealth and often linked to Mercury and Mars.
Formation
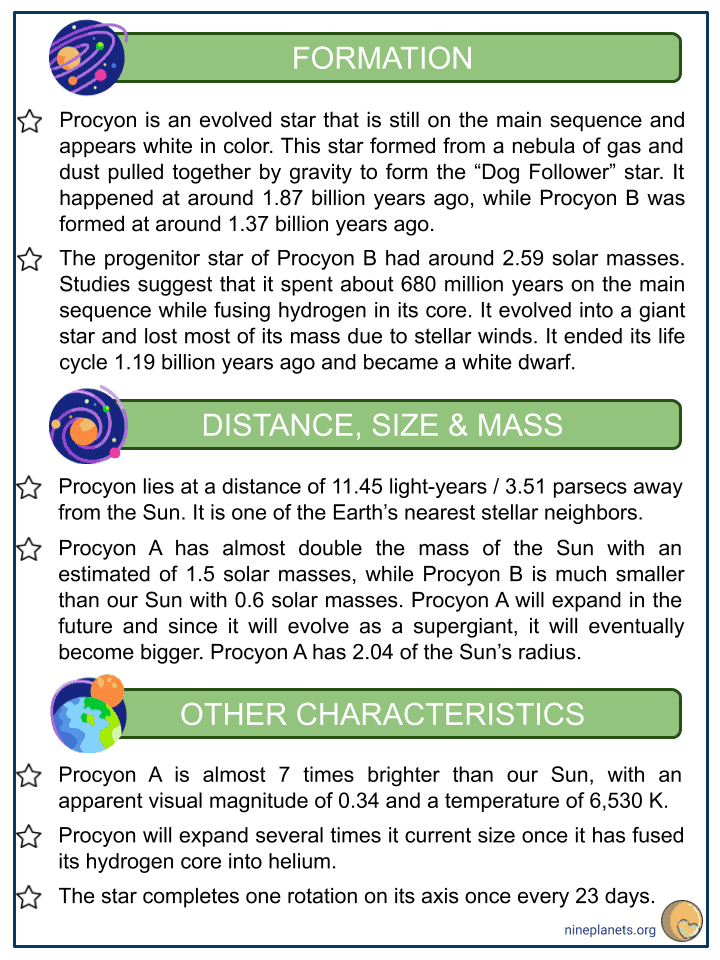
- Procyon is an evolved star that is still on the main sequence and appears white in color. This star formed from a nebula of gas and dust pulled together by gravity to form the “Dog Follower” star. It happened at around 1.87 billion years ago, while Procyon B was formed at around 1.37 billion years ago.
- The progenitor star of Procyon B had around 2.59 solar masses. Studies suggest that it spent about 680 million years on the main sequence while fusing hydrogen in its core. It evolved into a giant star and lost most of its mass due to stellar winds. It ended its life cycle 1.19 billion years ago and became a white dwarf.
Distance, Size & Mass
- Procyon lies at a distance of 11.45 light-years / 3.51 parsecs away from the Sun. It is one of the Earth’s nearest stellar neighbors.
- Procyon A has almost double the mass of the Sun with an estimated of 1.5 solar masses, while Procyon B is much smaller than our Sun with 0.6 solar masses. Procyon A will expand in the future and since it will evolve as a supergiant, it will eventually become bigger. Procyon A has 2.04 of the Sun’s radius.
Other Characteristics
- Procyon A is almost 7 times brighter than our Sun, with an apparent visual magnitude of 0.34 and a temperature of 6,530 K.
- Procyon will expand several times it current size once it has fused its hydrogen core into helium.
- The star completes one rotation on its axis once every 23 days.
Stellar System
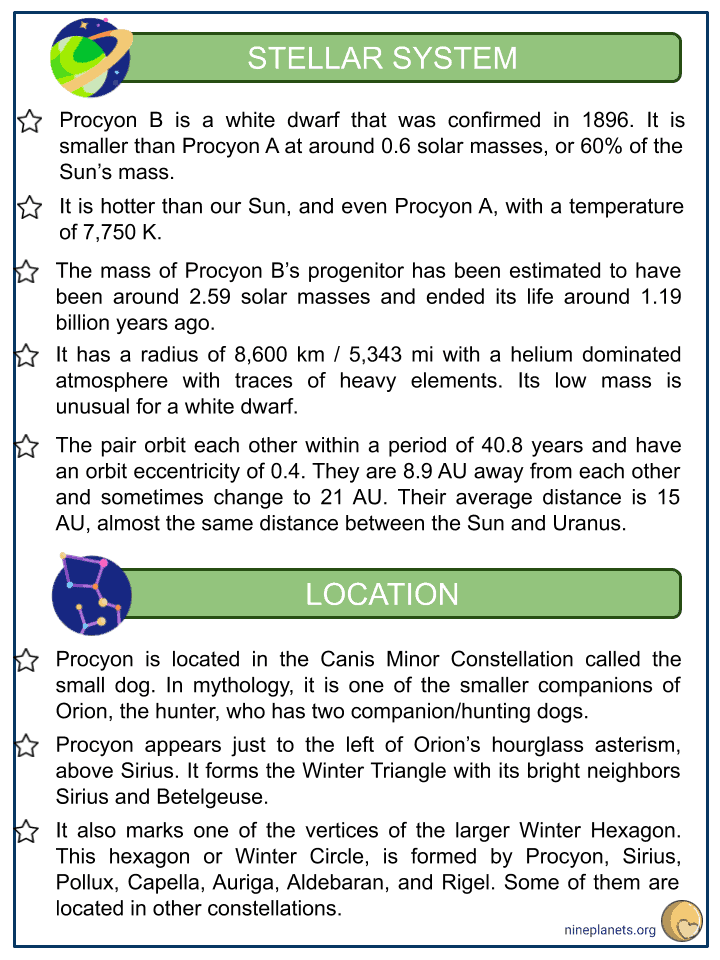
- Procyon B is a white dwarf that was confirmed in 1896. It is smaller than Procyon A at around 0.6 solar masses, or 60% of the Sun’s mass.
- It is hotter than our Sun, and even Procyon A, with a temperature of 7,750 K.
- The mass of Procyon B’s progenitor has been estimated to have been around 2.59 solar masses and ended its life around 1.19 billion years ago.
- It has a radius of 8,600 km / 5,343 mi with a helium dominated atmosphere with traces of heavy elements. Its low mass is unusual for a white dwarf.
- The pair orbit each other within a period of 40.8 years and have an orbit eccentricity of 0.4. They are 8.9 AU away from each other and sometimes change to 21 AU. Their average distance is 15 AU, almost the same distance between the Sun and Uranus.
Location
- Procyon is located in the Canis Minor Constellation called the small dog. In mythology, it is one of the smaller companions of Orion, the hunter, who has two companion/hunting dogs.
- Procyon appears just to the left of Orion’s hourglass asterism, above Sirius. It forms the Winter Triangle with its bright neighbors Sirius and Betelgeuse.
- It also marks one of the vertices of the larger Winter Hexagon. This hexagon or Winter Circle, is formed by Procyon, Sirius, Pollux, Capella, Auriga, Aldebaran, and Rigel. Some of them are located in other constellations.
The Future
- Procyon is too bright for its spectral class. This is an indicator that the star has almost run out of hydrogen in its core and has begun to expand as it continues to evolve into a subgiant.
- Studies suggest that it will continue to expand until it is 80 to 150 times its current size then turn orange or red at some point in the next 10 to 100 million years. Procyon A will end its life as a white dwarf, which is unlike Procyon B.
Did You Know?
- It is one of the 58 bright stars in the field of celestial navigation. Many of its neighbors are also in this class such as Sirius, Adhara, Betelgeuse, Rigel, Bellatrix, Alnilam, and Pollux.
- Procyon is often used in many works of fiction such as literature, films, television, and even video games such as Cabal online.
- The ancient Chinese knew Procyon as the Third Star of South River. South River was an asterism formed by Procyon, Gomeisa, and Epsilon Canis Minoris.
- One Arabic name for Procyon was Al Shira, which means the Syrian sign.
- The flag of Brazil features 27 stars with each one of them symbolizing a Brazilian Federation Unit. Procyon is one of these stars representing the state of Amazonas.
- To the ancient Egyptians, Procyon represented Nangar, an aspect of the god Marduk known as the carpenter. He rebuilt the heavens and organized the sky.
- In Macedonian folklore, Sirius and Procyon are known as “the wolves” or Volci, which circles around a plow with oxen represented by the Orion Constellation.