Download Deneb Algedi Worksheets
Click the button below to get instant access to these premium worksheets for use in the classroom or at a home.
This worksheet can be edited by Premium members using the free Google Slides online software. Click the Edit button above to get started.
Download free sample
Not ready to purchase a subscription yet? Click here to download a FREE sample of this worksheet pack.
Resource Examples
Click any of the example images below to view a larger version.
Key Facts & Information
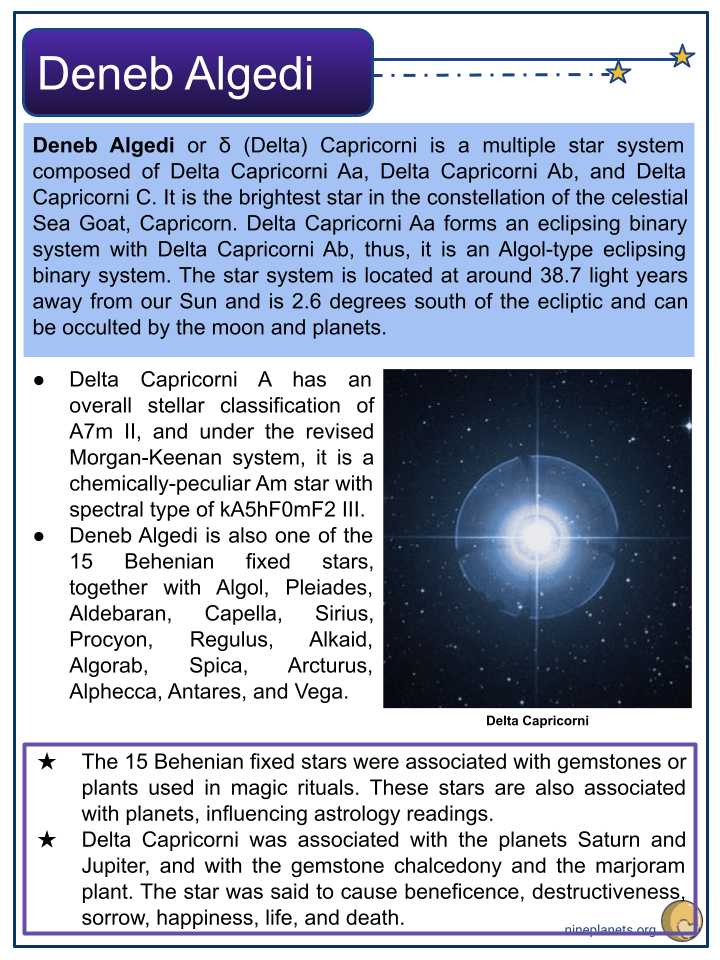
- Deneb Algedi or δ (Delta) Capricorni is a multiple star system composed of Delta Capricorni Aa, Delta Capricorni Ab, and Delta Capricorni C. It is the brightest star in the constellation of the celestial Sea Goat, Capricorn. Delta Capricorni Aa forms an eclipsing binary system with Delta Capricorni Ab, thus, it is an Algol-type eclipsing binary system. The star system is located at around 38.7 light years away from our Sun and is 2.6 degrees south of the ecliptic and can be occulted by the moon and planets.
- Delta Capricorni A has an overall stellar classification of A7m II, and under the revised Morgan-Keenan system, it is a chemically-peculiar Am star with spectral type of kA5hF0mF2 III.
- Deneb Algedi is also one of the 15 Behenian fixed stars, together with Algol, Pleiades, Aldebaran, Capella, Sirius, Procyon, Regulus, Alkaid, Algorab, Spica, Arcturus, Alphecca, Antares, and Vega.
- The 15 Behenian fixed stars were associated with gemstones or plants used in magic rituals. These stars are also associated with planets, influencing astrology readings.
- Delta Capricorni was associated with the planets Saturn and Jupiter, and with the gemstone chalcedony and the marjoram plant. The star was said to cause beneficence, destructiveness, sorrow, happiness, life, and death.
Nomenclature
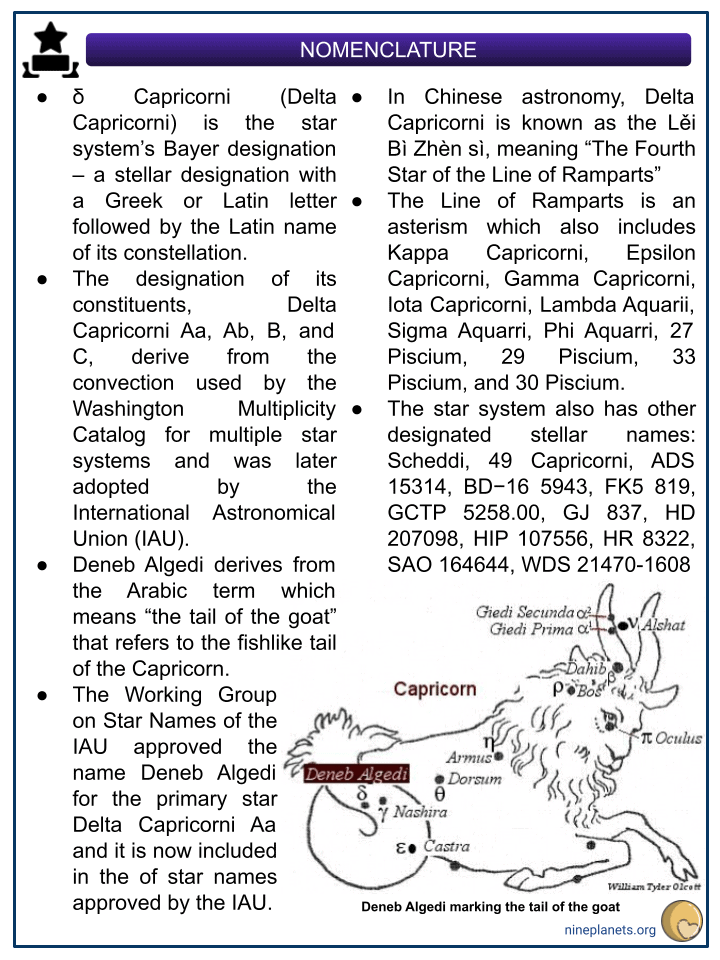
- δ Capricorni (Delta Capricorni) is the star system’s Bayer designation – a stellar designation with a Greek or Latin letter followed by the Latin name of its constellation.
- The designation of its constituents, Delta Capricorni Aa, Ab, B, and C, derive from the convection used by the Washington Multiplicity Catalog for multiple star systems and was later adopted by the International Astronomical Union (IAU).
- Deneb Algedi derives from the Arabic term which means “the tail of the goat” that refers to the fishlike tail of the Capricorn.
- The Working Group on Star Names of the IAU approved the name Deneb Algedi for the primary star Delta Capricorni Aa and it is now included in the of star names approved by the IAU.
- In Chinese astronomy, Delta Capricorni is known as the Lěi Bì Zhèn sì, meaning “The Fourth Star of the Line of Ramparts”
- The Line of Ramparts is an asterism which also includes Kappa Capricorni, Epsilon Capricorni, Gamma Capricorni, Iota Capricorni, Lambda Aquarii, Sigma Aquarri, Phi Aquarri, 27 Piscium, 29 Piscium, 33 Piscium, and 30 Piscium.
- The star system also has other designated stellar names: Scheddi, 49 Capricorni, ADS 15314, BD−16 5943, FK5 819, GCTP 5258.00, GJ 837, HD 207098, HIP 107556, HR 8322, SAO 164644, WDS 21470-1608
Observational History
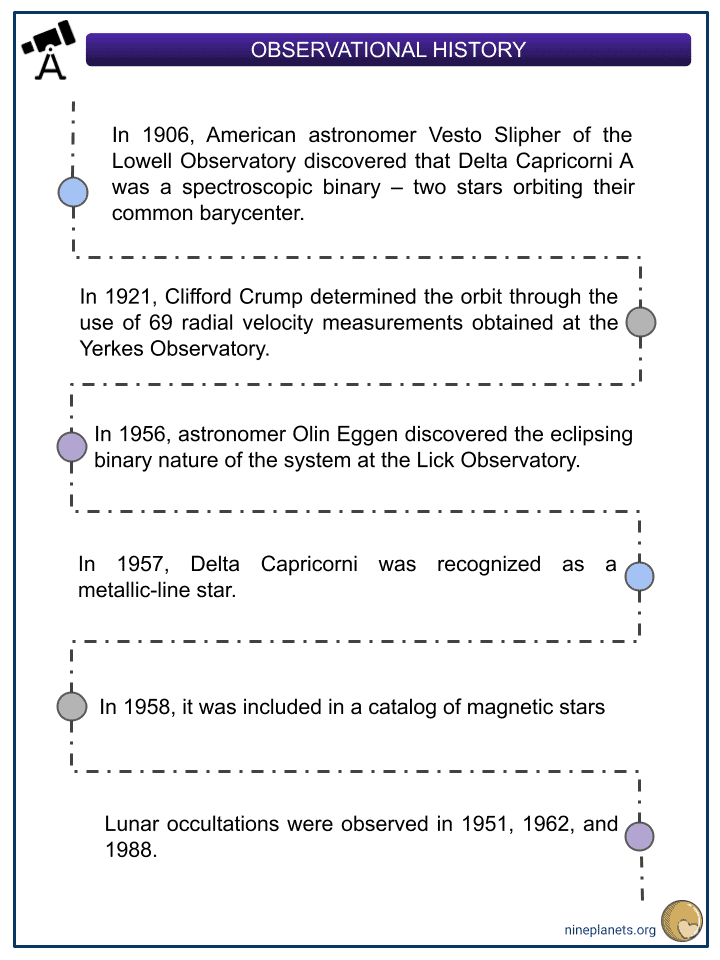
- In 1906, American astronomer Vesto Slipher of the Lowell Observatory discovered that Delta Capricorni A was a spectroscopic binary – two stars orbiting their common barycenter.
- In 1921, Clifford Crump determined the orbit through the use of 69 radial velocity measurements obtained at the Yerkes Observatory.
- In 1956, astronomer Olin Eggen discovered the eclipsing binary nature of the system at the Lick Observatory.
- In 1957, Delta Capricorni was recognized as a metallic-line star.
- In 1958, it was included in a catalog of magnetic stars
- Lunar occultations were observed in 1951, 1962, and 1988.
Properties
- The primary star, Delta Capricorni Aa, is much bigger than the Sun with a mass of 2 solar masses and a radius of 1.91 solar radii.
- The overall stellar classification of Delta Capricorni Aa, A7m III, indicates that it is a white giant star that has exhausted the supply of hydrogen inside its core.
- It is also a chemically-peculiar Am star with spectral type of kA5hF0mF2 III.
- This means that the calcium K-lines of the star matches the temperature of an A5 star (kA5), the hydrogen spectral type of an F0 star (hF0), and the metallic absorption lines of an F2 star (mF2).
- The surface temperature of the primary star is around 7.301 K, thus, 1.2 times hotter than the Sun.
- It is also an energetic star, being 8.5 times brighter than our Sun.
- Delta Capricorni Aa has an estimated surface gravity around 3.66 cgs.
- It is a fast spinner with a rotational velocity of 105 km/s, however, high rotational velocity is unusual for an Am star.
- The companion or the secondary star, Delta CApricorni Ab, is much smaller than the primary star with a mass of 0.73 solar masses and a radius of 0.9 solar radii.
- Delta Capricorni Ab is believed to be a G or K-type star.
- The average surface temperature of the secondary star is around 4,500 K.
- It also has an estimated parallax of around 84.27 milliarcseconds.
- The Delta Capricorni star system is located at around 38.7 light years away from our Sun. It is one of the brightest stars in the night sky which can be seen by the naked eye.
Stellar System
- Delta Capricorni A, consisting of the primary and the secondary stars, is an Algol-type eclipsing binary star with an orbital period of 1.022768 days with an inclination of 72.5°, close to our line of sight.
- Their orbit eccentricity has been assumed to be 0.
- The peak apparent magnitude of the star system is 2.81 and it varies in a range of -2.90 to 3.05.
- Its absolute magnitude has been determined to be +2.48.
- The magnitude reduces by 0.24 as the secondary star eclipses the primary star. On the other hand, it is reduced by 0.09 magnitude when the primary star eclipses the secondary star.
- The radial velocity of Delta Capricorni has been estimated to be around -6.3 km/s.
- Delta Capricorni has also been associated with extreme ultraviolet and radio sources, due to the coronal activity in the secondary star.
- There are two suggested optical companions.
- A 15th magnitude star 1 arcminute away with a solar luminosity of less than 6/100,000 and;
- A 13th magnitude star 2 arcminutes away with a solar luminosity of less than 1/100,00 and an increasing distance which raises the issue whether the receding stars are related to the primary star at all.
The Celestial Sea Goat
- Deneb Algedi is located in the constellation of the celestial Sea Goat, Capricornus.
- It marks the celestial tail of Capricornus.
- The constellation Capricornus is one of the 48 constellations listed in the 2nd century by the Greco-Roman astronomer Ptolemy.
- It is one of the faintest constellations in the sky though it is visible to the naked eye.
- Capricornus is the 40th biggest constellation in the night sky, with an area of 414 square degrees.
- The story of Capricornus originated with the Babylonians and Sumerians; they both knew it as the goat fish.
- In Greek mythology, Capricornus is sometimes identified as Amalthea, the goat that was suckled by the infant Zeus, after his mother, Rhea, saved him from his father, Cronos.
- Cronos had devoured his other children because of a prophecy that he would be overthrown by one of them.
- In the early Bronze Age, Capricornus marked the winter solstice, and in modern astrology, it is visible on the first day of winter.
Greek Mythology
- In Greek mythology, Capricornus is sometimes identified as Amalthea, the goat that was suckled by the infant Zeus, after his mother, Rhea, saved him from his father, Cronos.
- Cronos had devoured his other children, because of a prophecy that he would be overthrown by one of them.
- In the other story of Greek mythology, Capricornus is also sometimes identified as Pan, the god with a goat’s horns and legs, who helped scare the Titans away during the gods’ war with the Titans.
- He also warned the gods that Typhon, a monster sent by Gaia to fight the gods, was approaching, and suggested that the gods disguise themselves as animals.
- Pan saved himself from Typhon by jumping into the Nile river and turning his lower body into a fish.
- Zeus eventually killed typhon and Capricornus is still depicted as a goat with the tail of a fish.
Did You Know?
- Delta Capricorni is still not designated as the alpha star of the constellation Capricorn, even though it is the brightest star.
- The celestial objects in the constellation Capricornus observed in the northern hemisphere during the months of July to November are best seen during early September.
- In medieval astrology, Deneb Algedi was said to rule the blood vessels and nerve connections surrounding the vertebrae in the human body.
- The planet Neptune was first discovered near Delta Capricorni on September 23, 1846 by German astronomer Johann Galle.
- As one of the 15 Behenian fixed stars, Deneb Algedi was associated with the planets Saturn and Jupiter, and with the gemstone chalcedony and the marjoram plant, and was said to cause beneficence, destructiveness, sorrow, happiness, life, and death.
- In astrology, Capricorn is the 10th sign in the zodiac that represents those who were born between December 22 and January 19.
- Most information about Deneb Algedi’s origin and formation are still unknown.
- Its stars may have formed at the same time or at different times then somehow ended gravitationally bound to one another.
- Unlike some star systems, the stars are not associated with any known group of moving stars but they are likely formed from a molecular cloud of dust and gas.
- The system may be around 600 million years.
Future
- The primary star has already exhausted its hydrogen supplies inside its core, thus, is on its way to becoming a red giant.
- The temperatures will rise and its outer layers will continue to expand as its core collapses.