Download Canis Major Constellation Worksheets
Click the button below to get instant access to these premium worksheets for use in the classroom or at a home.
This worksheet can be edited by Premium members using the free Google Slides online software. Click the Edit button above to get started.
Download free sample
Not ready to purchase a subscription yet? Click here to download a FREE sample of this worksheet pack.
Resource Examples
Click any of the example images below to view a larger version.
Key Facts & Information
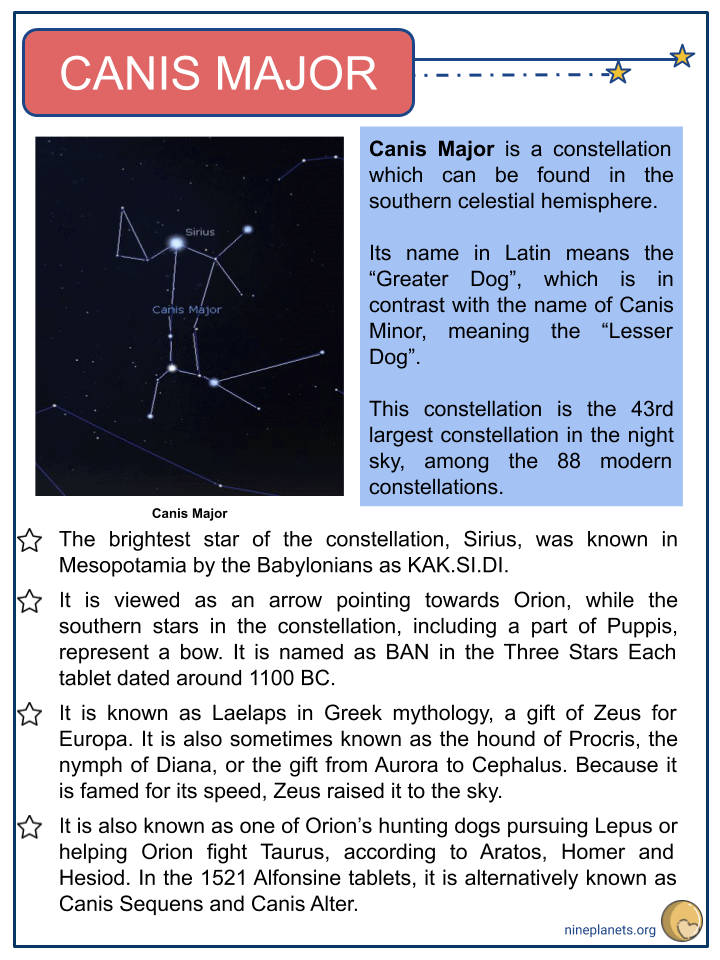
- Canis Major is a constellation which can be found in the southern celestial hemisphere.
- Its name in Latin means the “Greater Dog”, which is in contrast with the name of Canis Minor, meaning the “Lesser Dog”.
- This constellation is the 43rd largest constellation in the night sky, among the 88 modern constellations.
- The brightest star of the constellation, Sirius, was known in Mesopotamia by the Babylonians as KAK.SI.DI.
- It is viewed as an arrow pointing towards Orion, while the southern stars in the constellation, including a part of Puppis, represent a bow. It is named as BAN in the Three Stars Each tablet dated around 1100 BC.
- It is known as Laelaps in Greek mythology, a gift of Zeus for Europa. It is also sometimes known as the hound of Procris, the nymph of Diana, or the gift from Aurora to Cephalus. Because it is famed for its speed, Zeus raised it to the sky.
- It is also known as one of Orion’s hunting dogs pursuing Lepus or helping Orion fight Taurus, according to Aratos, Homer and Hesiod. In the 1521 Alfonsine tablets, it is alternatively known as Canis Sequens and Canis Alter.
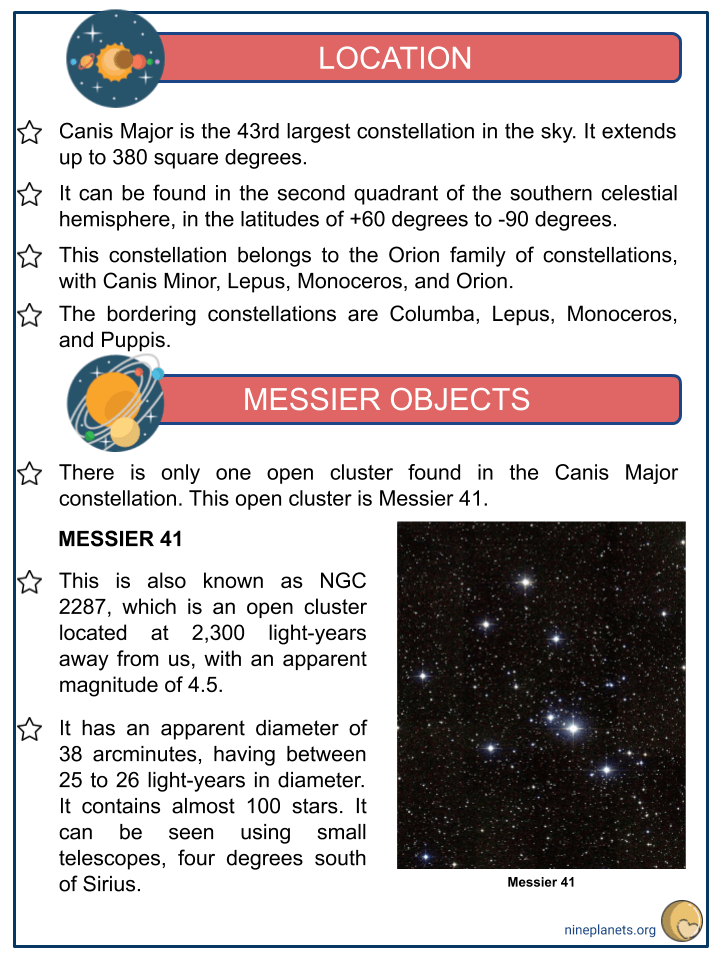
Location
- Canis Major is the 43rd largest constellation in the sky. It extends up to 380 square degrees.
- It can be found in the second quadrant of the southern celestial hemisphere, in the latitudes of +60 degrees to -90 degrees.
- This constellation belongs to the Orion family of constellations, with Canis Minor, Lepus, Monoceros, and Orion.
- The bordering constellations are Columba, Lepus, Monoceros, and Puppis.
Messier Objects
- There is only one open cluster found in the Canis Major constellation. This open cluster is Messier 41.
- MESSIER 41
- This is also known as NGC 2287, which is an open cluster located at 2,300 light-years away from us, with an apparent magnitude of 4.5.
- It has an apparent diameter of 38 arcminutes, having between 25 to 26 light-years in diameter. It contains almost 100 stars. It can be seen using small telescopes, four degrees south of Sirius.
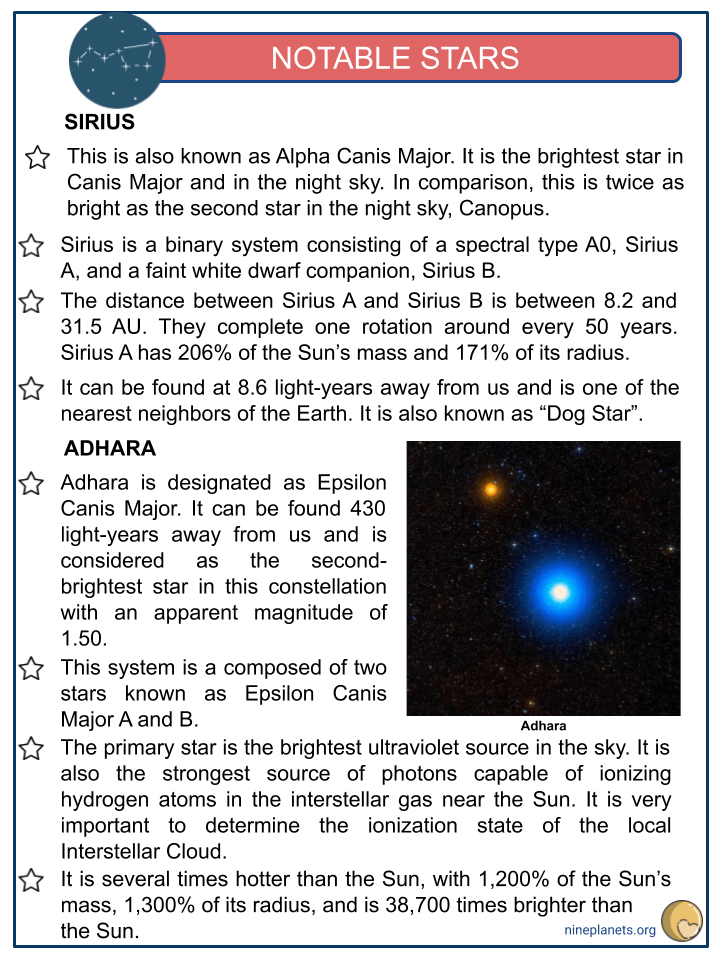
Notable Stars
- SIRIUS
- This is also known as Alpha Canis Major. It is the brightest star in Canis Major and in the night sky. In comparison, this is twice as bright as the second star in the night sky, Canopus.
- Sirius is a binary system consisting of a spectral type A0, Sirius A, and a faint white dwarf companion, Sirius B.
- The distance between Sirius A and Sirius B is between 8.2 and 31.5 AU. They complete one rotation around every 50 years. Sirius A has 206% of the Sun’s mass and 171% of its radius.
- It can be found at 8.6 light-years away from us and is one of the nearest neighbors of the Earth. It is also known as “Dog Star”.
- ADHARA
- Adhara is designated as Epsilon Canis Major. It can be found 430 light-years away from us and is considered as the second- brightest star in this constellation with an apparent magnitude of 1.50.
- This system is a composed of two stars known as Epsilon Canis Major A and B.
- The primary star is the brightest ultraviolet source in the sky. It is also the strongest source of photons capable of ionizing hydrogen atoms in the interstellar gas near the Sun. It is very important to determine the ionization state of the local Interstellar Cloud.
- It is several times hotter than the Sun, with 1,200% of the Sun’s mass, 1,300% of its radius, and is 38,700 times brighter than the Sun.
- WEZEN
- This is also known as Delta Canis Majoris, a yellow-type F-type supergiant and the third-brightest star in the constellation. It has an apparent magnitude of 1.824.
- It has been one of the stable anchors for the classification of other stars since 1943. It is located at 10 degrees south southeast of Sirius.
- It has 1,690% of the Sun’s mass, around 21, 500% of its radius, and is 82,000 times brighter than the Sun. It is located 1,600 light-years away from the Sun. In the future it will become a red supergiant.
- MIRZAM
- Mirzam is the fourth-brightest star in the constellation and designated as Beta Canis Majoris. It is a blue-white giant with an apparent magnitude of 1.985. It is located at around 490 light-years away from us.
- Its magnitude varies at +1.97 and +2.01 over a six hour period. It is 1,350% bigger than the Sun, having 970% of its radius. It is 26,600 times brighter than the Sun. It is located near the far end of the Local Bubble, a cavity in the local interstellar medium where the Sun is also traveling.
- ALUDRA
- Aludra is the fifth-brightest star in the constellation and designated as Eta Canis Majoris with an apparent magnitude of 2.450. This is also one of the stable anchor points by which other stars have been classified since 1943.
- It a blue-white supergiant star with 1,919% of the Sun’s mass, 5,630% of its radius, and around 105,442 time brighter. It is an Alpha Cygni variable star with its brightness varying from +2.38 and +2.48 over a period of 4.7 days. It is located at around 2,000 light-years away.
- TAU CANIS MAJORIS
- This is a multiple star system located at around 5,000 light-years away from us. It is the brightest member of the open cluster NGC 2362 with an apparent magnitude of 4.40.
- The primary star is 5,000% times bigger than the Sun, with 1,980% of its radius and is 280,000 times brighter than the Sun. It has surface temperatures of around 32,000 K.
- FURUD
- This is the sixth-brightest star in the constellation and designated as Zeta Canis Majoris. It is a spectroscopic binary star with a +3.015 apparent magnitude.
- The primary star is a main-sequence star with 770% of the Sun’s mass and 390% of its radius. It is also 3,603 times brighter than the Sun. It is 362 light-years away from us and has a temperature of 18,700 K.
- MULIPHEIN
- Muliphein is a blue-white B-type bright giant star which is designated as Gamma Canis Majoris. It is 440 light-years away from us.
- This star has an apparent magnitude of +4.10.
- This star has abnormal lines of magnesium and mercury in its spectrum. It has 560% of the radius of the Sun. It is also twice as hot as the Sun with a temperature of 13, 596 K.
- Muliphein is a member of an open cluster which is called Collinder 121.
- OMICRON1
- Omicron1 is a red supergiant star located 3,500 light-years away from us. It is an irregular variable star with a varying magnitude of 3.78 and 3.99.
- It is 16,000 times brighter than the Sun, with 783% of its mass and 21,200% of its radius. It is expected that this star will explode in the near future as a type II supernova.
- OMICRON2
- This is the seventh-brightest star in the constellation with an apparent magnitude of 3.043. It can be found at around 2,800 light-years away from the Earth.
- It is 220,000 times brighter than the Sun with 2,140% of its mass and 6,500% of its radius. It is classified as a massive supergiant of spectral type B3, which appears blue in color.
- RXJ0720.4-3125
- This is a neutron star which was first discovered in 1997 in a ROSAT All-sky survey. It is a small star located 1,200 light-years away from us.
- It is a part of the Magnificent Seven, which is a group of neutron stars located near the Solar System.
- It has an apparent magnitude of -26.6 and a radius of around 5 km / 3.1 mi. Its temperatures vary wildly. The reason for this is still unknown.
- VY CANIS MAJORIS
- It is among the largest stars in the night sky to be discovered. This is a red supergiant located 3,900 light-years away from us.
- VY Canis Majoris has 1,700% of the Sun’s mass and 142,000% of its radius. It is one of the brightest stars, about 270,000 times brighter than the Sun. It is estimated to be cooler than the Sun with a temperature of 3,490 K.
- It has an apparent magnitude of 6.5 to 9.6. It is also fast spinning with a velocity of 300 km / 186.4 mi per second.
- This star is quite young. It is only 8.2 million years old, but it will not live long. It will soon explode as a hypernova, an event stronger than the supernova.
- IOTA CANIS MAJORIS
- It is a blue-white supergiant located 3,100 light-years away. It has an apparent magnitude of 4.40, but it varies from 4.36 to 4.40.
- It is 4,700 times brighter than the Sun, with 1,250% of its mass, and 2,590% of its radius. It is also three times brighter than the Sun with a temperature of 17,000 K.
- W CANIS MAJORIS
- This is a carbon star located at around 18,000 light-years away from the Earth. It has an apparent magnitude that varies slowly and irregularly from 6.35 to 7.90.
- It has carbon and s-process elements drawn to its surface during thermal pulses of its helium-burning shell. It is 3,560 times brighter than the Sun and has 23,400% of its radius. It is also cooler at only 2,900 K.
- EZ CANIS MAJORIS
- It is a binary star system which is located 4,900 light-years away from us. Its primary star is a Wolf-Rayet star, and among the top ten brightest Wolf-Rayet stars.
- It has an apparent magnitude that changes from 6.71 to 6.95 over a period of 3.76 days. It is 620,000 times brighter than the Sun. It is also several times hotter, with a temperature of 89,100 K. EZ Canis Majoris has 2,300% of the Sun’s mass and 325% of its radius.
- HD 56925
- This is also a Wolf-Rayet star designated as WR 7. It is located 17,000 light-years away from us. It lies at the center of a complex bubble of gas, which is shocked and somewhat ionized due to the star’s radiation and winds.
- It is the ring nebula NGC 2359 also known as Thor’s Helmet. It has an apparent magnitude of 11.4. It is 229,000 times brighter than the Sun. It has around 1,300% of its mass and 126% of its radius. It is 19.3 times hotter than the Sun with a temperature of 112,000 K.
Deep-Sky Objects
- NGC 2360
- This is also known as Caroline’s Cluster or Caldwell 58, an open cluster located 3,700 light-years away from us. It has an apparent magnitude of 7.2 and a diameter of 15 light-years. It also contains many red giant stars.
- Caroline’s Cluster was discovered by Caroline Herschel in 1783. Some say that this cluster is at around 2.2 billion years old.
- NGC 2362
- It also called Caldwell 64. This is a big open cluster with more than 500 solar masses with an apparent magnitude of 4.1 and a radius of 11.2 light-years.
- It is said to have been discovered in 1654. Tau Canis Majoris is the brightest star in this cluster, thus, it is sometimes referred to as Tau Canis Majoris cluster. This cluster is in relation with Sh2-310, a giant nebula.
- NGC 2354
- This is a relatively faint open cluster that contains 15 stars that are visible through binoculars. It has an apparent magnitude of 6.5.
- NGC 2359
- NGC 2359 is also called Thor’s Helmet or Duck Nebula. This is an emission nebula which is located 11,960 light-years away from us. It has a radius of 30 light-years.
- Inside NGC 2359 is a Wolf-Rayet star which is WR 7. It is an extremely hot star and illuminates the surrounding area.
- In this nebula, there are a hundred solar masses of ionized materials and unionized gas.
- NGC 2207 & IC 2163
- These two are a pair of colliding spiral galaxies which are located at around 80 light-years away from the Earth. NGC 2207 is the bigger galaxy and is classified as an intermediate spiral galaxy.
- On the other hand, IC 2163 is a barred spiral galaxy. They have an apparent magnitude of 12.2 and 11.6 respectively. The collision of these two galaxies are important to astronomers because this might reflect the possible fate of the Milky Way galaxy and the Andromeda galaxy.
- CANIS MAJOR DWARF GALAXY
- This is also called Canis Major Overdensity. It is the closest satellite galaxy of the Milky Way to the Earth. It is an irregular galaxy located at 25,000 light-years away from us.
- It is estimated to have 1 billion stars, many of which are red giants. It is located 42,000 light-years away from Galactic Center.
Did You Know?
- In Chinese Astronomy, the whole constellation of Canis Major is located in the Vermillion Bird.
- For the Maori and Tuamotus people, Canis Major is recognized as a distinct entity.
- Sirius, a character from Harry Potter, is believed to be inspired by Canis Major. This character transforms into a dog.
- The rising of Sirius marked to flooding of the Nile River in Ancient Egypt.