Working through the lesson below will help your child to understand the effects of transformations (translations, rotations and reflections) on coordinates in a Cartesian plane.
Learning Takeaways: After this lesson, students will be able to understand the effects of:
- translations on coordinates in a Cartesian plane.
- rotations on coordinates in a Cartesian plane.
- reflections on coordinates in a Cartesian plane.
Important Vocabulary
Isometry: An isometry is a transformation that maintains congruency. This means that the transformation does not change the figure’s size or shape.
Make sure your child is familiar with the Cartesian coordinate system including the horizontal x-axis, the vertical y-axis, and the (x,y) convention used for locating points.
If you have not already done so, you may wish to review this congruency lesson with your child.
Translations
This section will help your child to translate congruent figures on a Cartesian plane. It will also introduce translation vectors which show the distance and direction of the translation.
Translations

Figure J is the pre-image. Figure S is translated.
A figure is a translation if it is moved without rotation.
Translation Vector
A Translation Vector is a vector that gives the length and direction of a particular translation. Vectors in the Cartesian plane can be written (x,y) which means a translation of x units horizontally and y units vertically.

Vectors translations can be written as shown in either of these two ways:

This vector can be said to be ray AB or vector D.
You translate a figure according to the numbers indicated by the vector. So if one point on a figure has coordinates of (-3,3) and the translation vector is (-1,3), the new coordinate is (-4,6). You add or subtract according to the signs in the numbers in the vector.
Work through the two examples below with your child to see how to apply translation vectors.
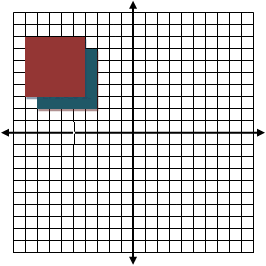
The red square’s coordinates are:
(-4,3); (-4,8); (-9,3); (-9,8).
What are the coordinate pairs under a translation vector of (1,-1) as shown by the blue square?
The new coordinates are:
(-3,2); (-3,7); (-8,2); (-8,7).
You can see that the translation did not move the figure far because the vector translation is small.

We will try a different vector translation of (3,-9) on the same red square
The new coordinates are:
(-1,-6); (-1,-1); (-6,-6); (-6,-1).
Get you child to try the next example. Do not look at the answer until he or she has tried to work it through the task.
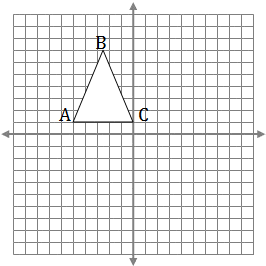
Task: Translate ΔABC with a vector translation of (6,-2)
Steps:
- Find the coordinates of Δ ABC.
- Add 6 to the X coordinates and subtract 2 (or add -2) from the Y coordinates.
- Plot the new coordinates on the grid.
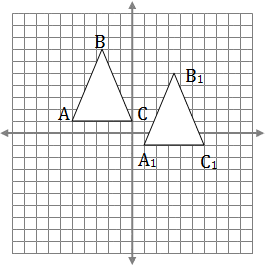
Answer and Explanation
Coordinates of ΔABC are:
(-5,1); (-2.5,7); (0,1)
Add 6 and subtract 2
A1 = (-5 + 6, 1 – 2) = (1,-1)
B1 = (-2.5 + 6, 7 – 2) = (3.5,5)
C1 = (0 + 6, 1 – 2) = (6,-1)
Plot ΔA1B1C1
Rotations
This section will show your child how to rotate a figure about the origin on a Cartesian plane. Work through the two examples below:
Note: Make sure your child knows that the origin is the intersection of the X and Y axes; (0,0) on the Cartesian plane.
Rotation Transformation: Example 1
Look at the four triangles on the Cartesian plane below. Each one is rotated about the origin as shown in the table.
| Triangle B | Triangle C | Triangle D |
| 90° rotation of Triangle A about the origin | 90° rotation of Triangle B about the origin | 90° rotation of Triangle C about the origin |
| 180° rotation of Triangle A about the origin | 180° rotation of Triangle B about the origin | |
| 270° rotation of Triangle A about the origin |

| The coordinates are: | |||
| Triangle A | (-2,2) | (-10,2) | (-6,8) |
| Triangle B | (2,2) | (2,10) | (8,6) |
| Triangle C | (2,-2) | (10,-2) | (6,-8) |
| Triangle D | (-2,-2) | (-2,-10) | (-8,-6) |
| Note the pattern in the coordinates for corresponding vertices on the triangles. |
Rotation Transformation: Example 2

Reflections
This section will help your child to reflect a figure over an axis on a Cartesian plane
Work through the two reflection examples below.
Reflection Transformation: Example 1

Reflection Transformation: Example 2
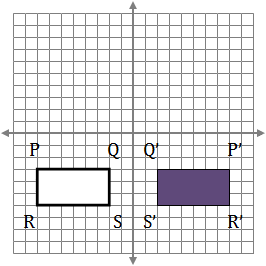
Discuss with your child how, when reflecting a figure over the x-axis, the figure remains the same distance from the y-axis and the y-coordinate therefore does not change. Similarly, when reflecting a figure over the y-axis, the figure remains the same distance from the x-axis and the x-coordinate therefore does not change.
Transformations Worksheets
Click the links below and get your child to try the transformation worksheets that will allow for practice with questions based on what is shown above.









